By Howard Lee
The poster sessions that I have attended over last 3 days at CLEO have been great (the only recommendation I might add is that it would have been really nice if they taken place closer towards the end of the day). The quality of the posters are very high, I enjoyed them immensely.
Another important highlight of the conference today was the postdeadline session where scientists present their latest and most impressive results in a 10 minute time frame. Here are a few that I heard:
Optical Broadband Angular Selectivity (JTH5B.2)
Yichen Shen from MIT presented their results on achieving broadband angular selectivity of light. The principle behind is to use the generalized Brewster angle by making 1D photonic crystal (multilayer structure made with SiO2 and Ta2O5) with different periodicity. He showed that a complete transparency of the structure at only one angle and the light reflects at other angles. The works are published at Science 343, 1499 (2014).
Silicon-Chip Mid-Infrared Frequency Comb Generation (STH5C.6)
Researcher from Cornell presented a first on-chip integrated mid-infrared frequency comb with 750nm-wide comb centered at 2.6um. Due to the large nonlinear loss of silicon from the three-photon absorption followed by free carrier generation, it was typically difficult to generate an efficient comb at mid-infrared region using silicon waveguide. The design of silicon waveguides with a ring resonator embedded in a PIN structure significantly reduce the free carrier lifetimes and allow the generation of mid-infrared frequency comb for the first time (see figure below).
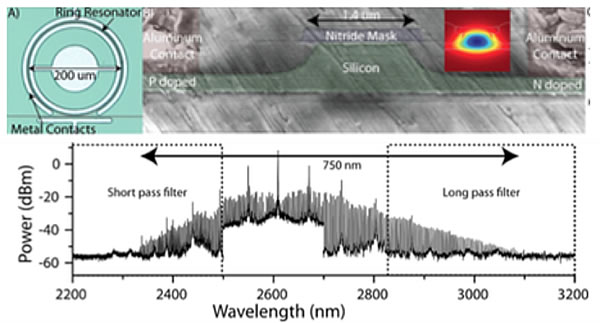
(Top) Optical microscope image of ring resonator with metal contacts and false colored SEM image of the silicon waveguide, doped regions, and metal contacts. Inset: simulated optical mode at 2.6 um, showing highconfinement. (Bottom) FTIR scans showing the full extent of the MIDIR frequency comb (corrected for the filters spectral response). [STH5C.6]
Gain from Helium-Xenon Discharges in Hollow Optical Fibres at 3 to 3.5 um (STh5C.10)
Researchers from Bath University discussed the first detected gain on laser transition in hollow core photonic crystal fiber gas discharges. They used an anti-resonant guided hollow core fiber for this discharge experiment as this fiber allow good transmission in IR range. They used fiber with length between 0.5-1m and high DC voltage up to 40kV to discharge the Helium-Xenon gas inside the fiber. They observed strong emission line from the discharge and found that the emission was stronger with longer fiber length, indicting the presence of net gain from the discharge. Their goal of the project is to make the first electrically excited fibre-based gas laser.
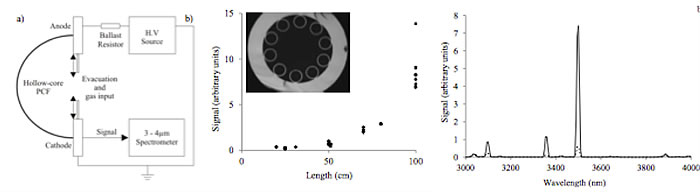 Experimental setup. b) Signal in a 20 nm bandwidth at 3.5 μm, with discharge current 0.25 mA at 12 mbar pressure, for different lengths Inset: Optical micrograph of the fibre. Spectra for 1 m length (solid) and 0.5 m length (dashed) discharges with a discharge current of 0.25 mA and 20 nm resolution. (STh5C.10).
Experimental setup. b) Signal in a 20 nm bandwidth at 3.5 μm, with discharge current 0.25 mA at 12 mbar pressure, for different lengths Inset: Optical micrograph of the fibre. Spectra for 1 m length (solid) and 0.5 m length (dashed) discharges with a discharge current of 0.25 mA and 20 nm resolution. (STh5C.10).
This has really been an enriching experience with great research in a number of areas. I look forward to seeing everyone next year, 10-15 May 2015.
Posted: 14 June 2014 by
Howard Lee
| with 0 comments